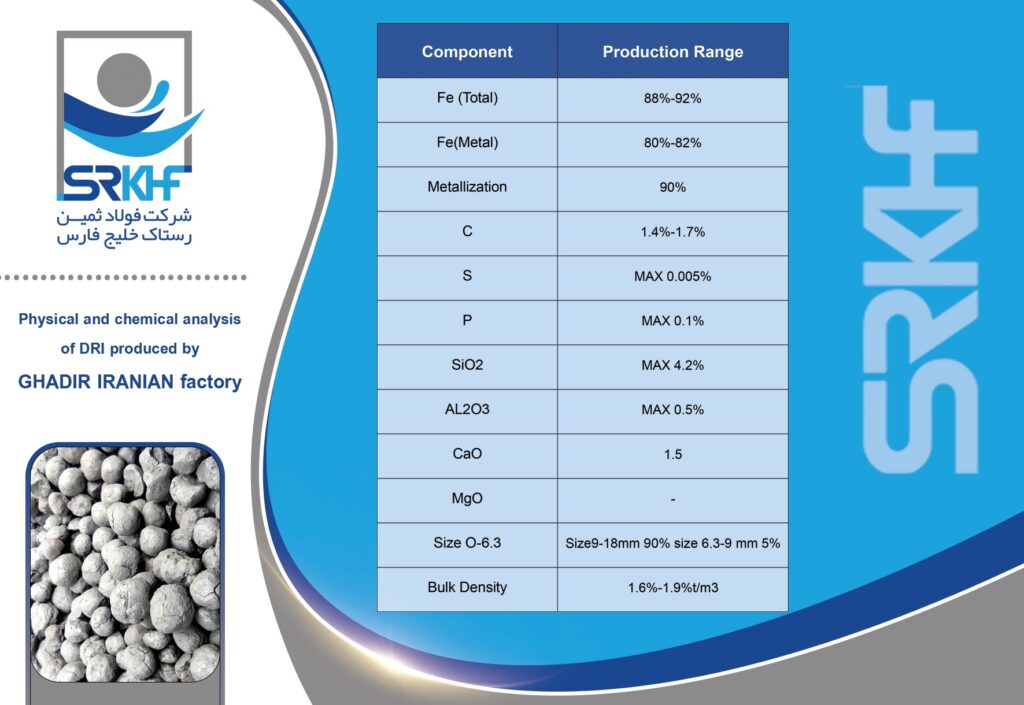
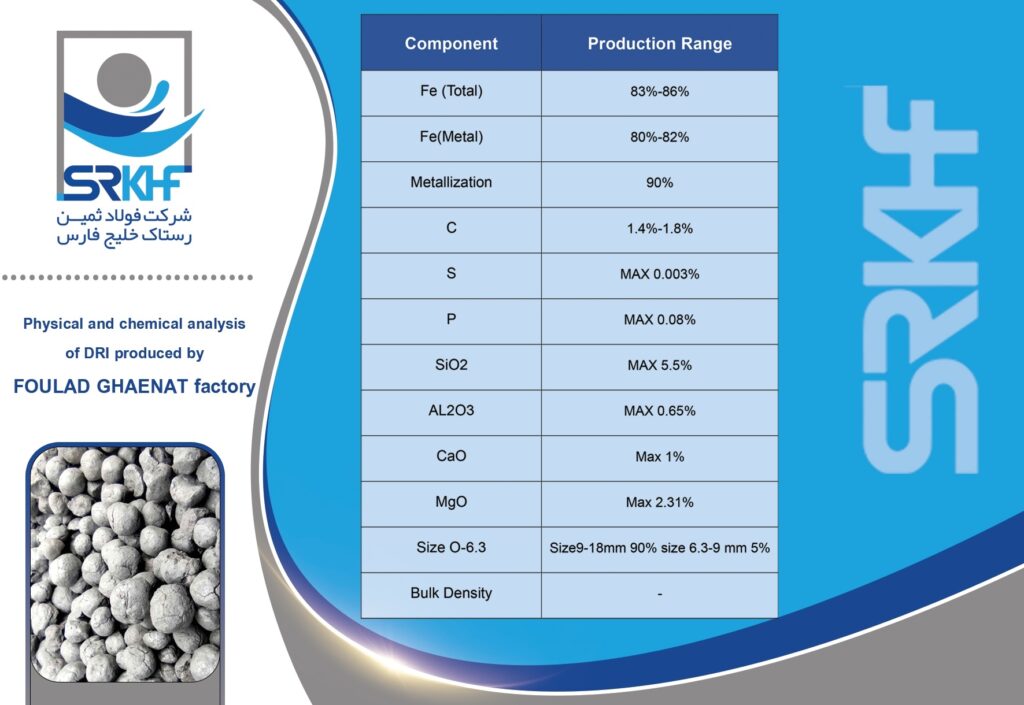
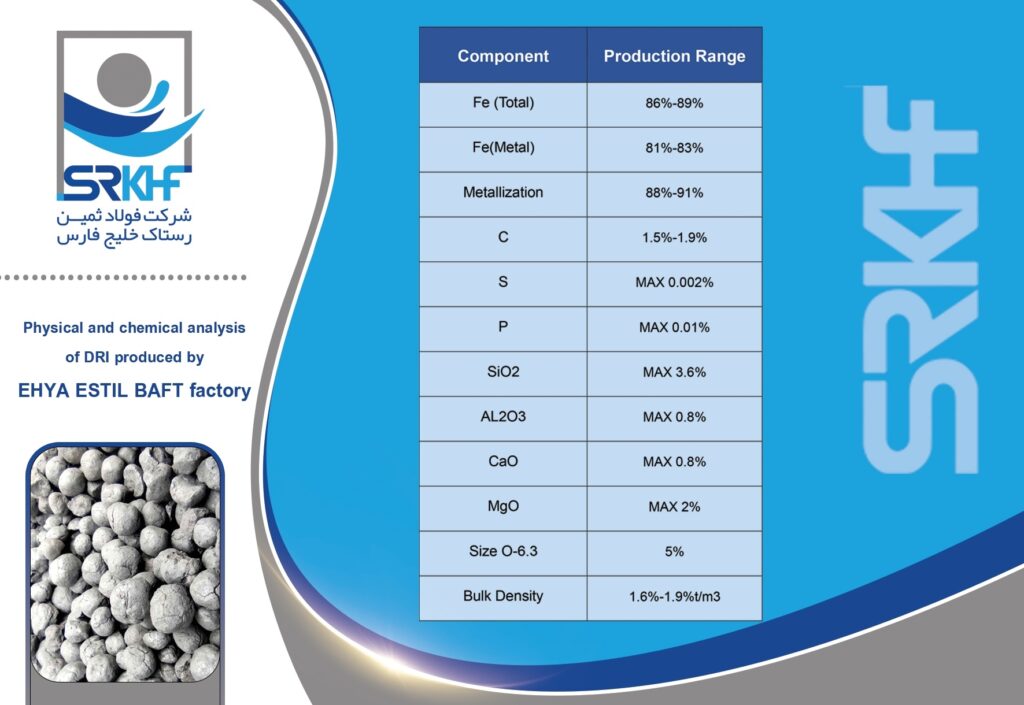
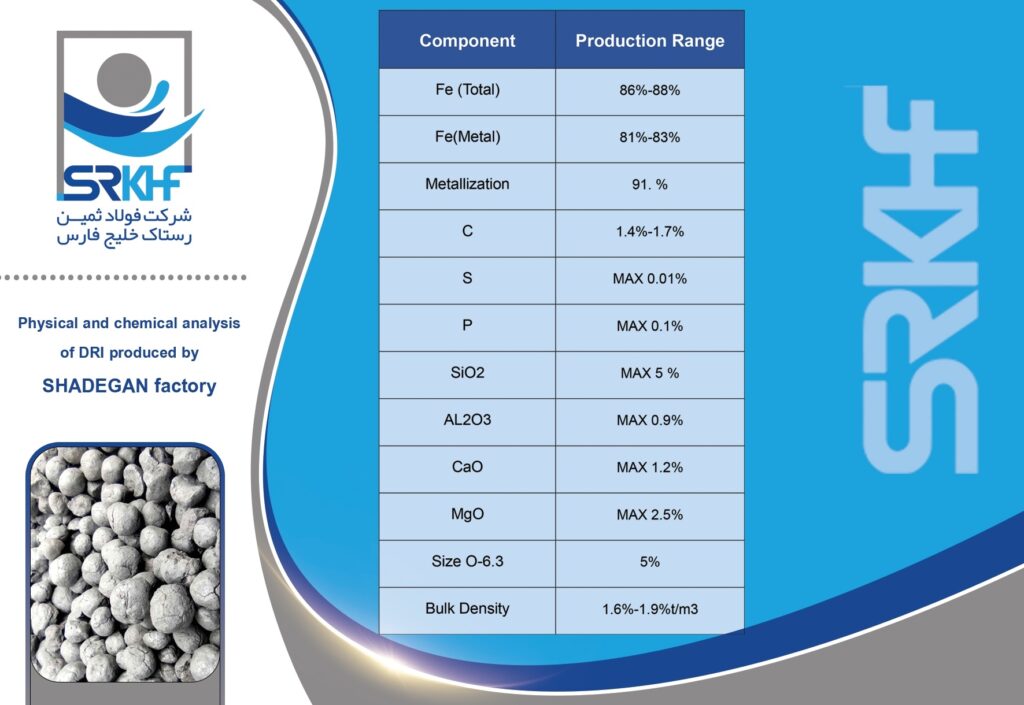
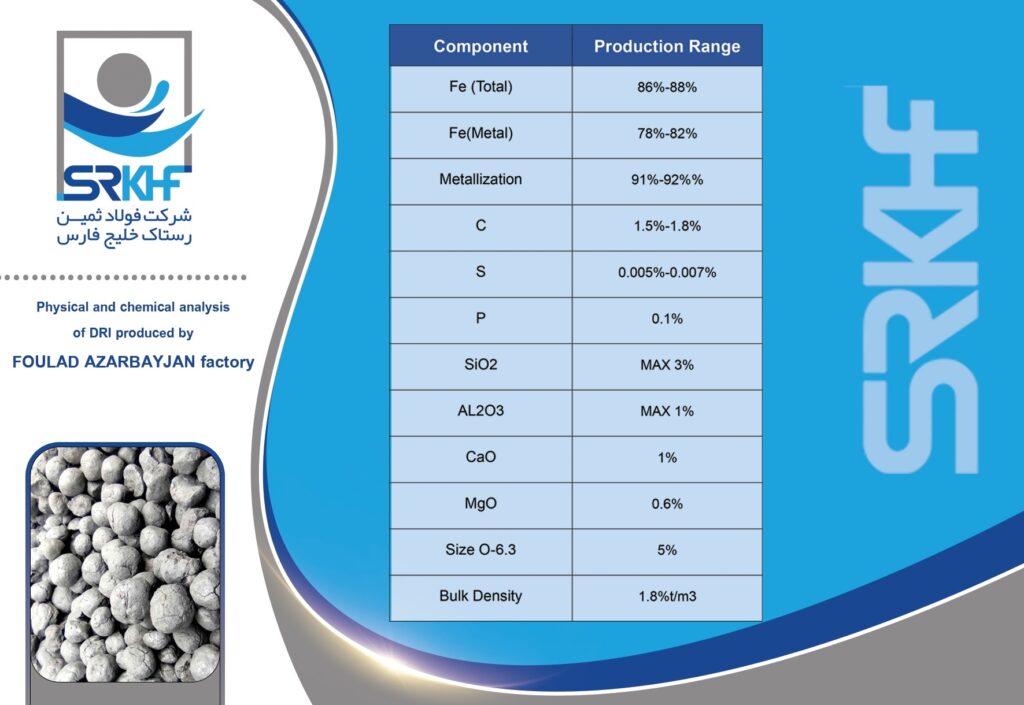
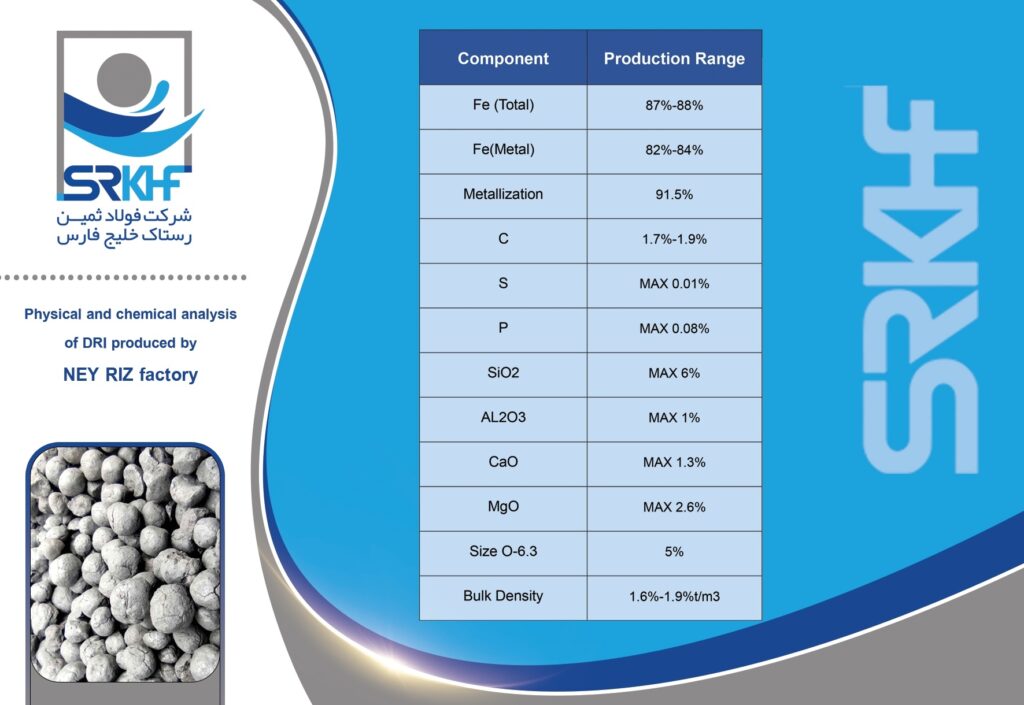
Sponge iron is a type of reduced iron that is obtained by direct reduction of iron ore (usually iron ore pellets) without completely melting it. This direct reduction process is usually carried out using natural gas or coal. This name is given because during the production process, oxygen is removed from the iron ore, leaving behind a porous, spongy structure. This porous structure makes it easy to melt in furnaces.
Sponge iron production generally has two main procedures:
Gas Based Method:
- In this method, natural gas is used as the reducing agent. This method is more common and more suitable for high-volume sponge iron production.
Coal Based Method
- In this method, coal is used as the reducing agent. This method is usually used for smaller capacities and in areas where natural gas is less available.
Main application of sponge iron
sponge iron is mainly used as a substitute for scrap iron in steelmaking furnaces (especially electric arc furnaces). Sponge iron improves the quality of the produced steel, as it contains fewer impurities than scrap iron.
Main application of sponge iron
- High purity: fewer impurities than scrap
- Quality consistency: its quality is more uniform than scrap collected from different sources.
- Reduceing pollution: its production process is less polluting than the production of pig iron (cast iron) in a blast furnace.
- Overall, sponge iron is a vital raw material in the modern steel industry and plays an important role in producing high-quality and clean steel.